Event viewer is a built in snap in windows operating system to log errors, changes, warnings and information. It will list events of services, applications and security events of the operating system. These events are helpful to identify a system issue or root cause of an ongoing error. And according to the events troubleshooting practice can be started.
Event viewer is a popular tool in windows so actually it doesn’t need an introduction, but most of the administrator’s does not get full use of it when come to troubleshoot. From this post I’m going to explain the features of event viewer and how to use it effectively to identify and troubleshoot an issue.
Ease of access
Event viewer can be accessed by all programs – Administrative Tools – Event Viewer or simply by typing “eventvwr” in Run.
Event types
Event viewer divided events according to following log files
- Application Logs -Records events logged by applications and programs such as SQL Server errors, Application crashes
- Security Logs – records events set by Audit policies. Valid or invalid logon attempts, file access create open or delete files. security logs are critical when required to track down logon attempts.
- System Logs – Records events generated by Operating system issues, failure to start a service, unexpected system restarts. Ect.
When the server is installed with specific roles, events according to the role is further divided in to its specific roles. Like
- Active Directory – Events specific to active directory
- KMS – Events specific to Key management system
- DNS – DNS related events.
- Directory Services – Active directory replication specific

Event Operations
- Search for events
Event viewer generate bulk of events in some short period of time. So to troubleshoot a issue, related events need to be filtered form the event log file. There are few options to segregate the events.
Find option is useful when identifying an event using a keyword. This is less complex.
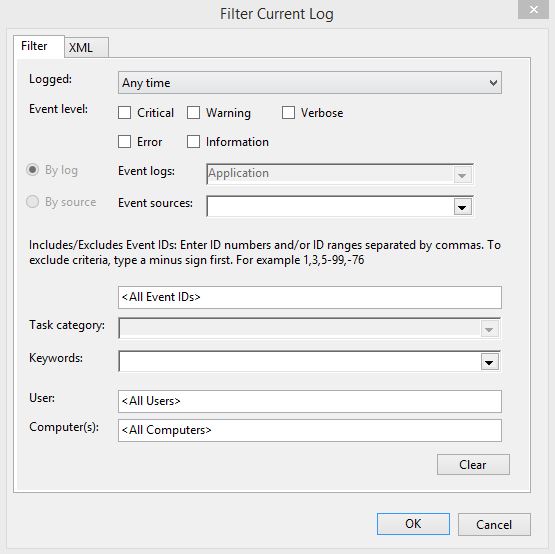
Event filtering is much broader rather than find. Using filtering you can filter event on event level, Event ID, Event source, keyword and computer name. If you know the event id, you can use it to get all the events and start the troubleshoot on event generated time or event source. Select Filter current log from action panel.
- Attach a task to an event
When a specific event is generated, a task can be triggered to run. Such as an email is send when an unexpected server shutdown event generated. Or message displayed when a service failed to start.
This is really easy to configure, and it can be useful in day to day Operations.
- Select the event you want to trigger the task, click attach a task to this event from actions
- Use following steps to send an email to a specific event.



- Create Custom views
Event viewer custom views are helpful when you want to group all events of a particular application or a service. It’s useful when you identified a problem and need to monitor it closely. And it’s really easy to implement.
- Select Create custom view from action panel, Custom views can be created by Event log type or source of the event.

- Select the event source or event log type.

- Press ok to set the custom view.
Export the event log
When it’s required to escalate an issue or asking technical help from a 3rd party, you can send the exported event log for troubleshoot. This is save time and no need to provide the remote access. Events logs can be saved by selecting save all events as from action panel.

Manage Event logs
- Change event log size
By default windows event log Maximum file size is defined as 20Mb’s. After it reach the defined value, it will over right the historical events with the latest ones. When it’s a critical system or a domain controller, best practice is to save logs for at least 6 months. So to maintain this, you have to increase the maximum log file size.
Microsoft has recommended maximum event log file size for windows server 2008 and above is 4GB. Regarding how critical is the log file to the company and the relevant time period, you can select the size of the log file. Event log size can be changed using event properties or Group policy.
- Change using event properties
Right click on event log and select properties. Change the log size. If you want, change the log path.

This option you have to server by server and event log file by file. If required to change this in a number of servers, as an example all the domain controllers, using a Group policy is the best option.
Using GPO
Using New GPO you can define the event log size to many number of servers, if you edit he default domain controllers GPO, all the domain controllers Event log file sizes can be modifies. Use the following GPO path and edit.
Computer Configuration->Policies->Administrative Templates->Windows Components->Event Log Service
- Event Subscription
When you want to collect events from multiple other computers event subscription can be used. Event subscription is helpful, when troubleshooting require to examine set of events from multiple logs on multiple computers. When event subscription configured, it will collect events from other defined computers (sources) to the event viewer which is subscription configured. This make easy to view all the related events and examine all together.
Before configuring Event subscription, both event collector and event forwarding computers (source) should be configured to support event subscription. Please refer the following TechNet article.
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc748890.aspx?f=255&MSPPError=-2147217396
- To create a new event subscription, go to the event viewer, from action panel select create subscription

- Use the select computer button to select the event source computers.
- To filter the forwarding events, use select events button.









