Nowadays, customer requirements are changing faster than ever in the competitive business environment. Software applications need to adjust to changing business conditions. Therefore, IT firms cannot limit software development only to the development phase. Maintenance and future updates are essential after releasing the software application into the deployment environment. When customers demand new changes to the system, development teams must respond with the fastest possible solutions. To achieve a higher level of efficacy in application management requires maintaining a good communication channel between all parties and high transparency throughout the entire application lifecycle. Organizations can accomplish these goals by adopting the Application Lifecycle Management (ALM). Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) uses to manage the different stages of the lifespan of a product. Likewise, ALM provides a framework to manage application development.
What is Application Lifecycle Management?
Application Lifecycle Management is the process of managing a software application from the outset to the end of life. It begins with the understanding of the customers' needs. Then continues over the entire lifecycle until the application decommissioned its operations. By adopting ALM, organizations try to link software engineering practices with business management strategies. ALM integrates people, tools, and processes that are virtually related to application development to achieve this. An effective ALM model consists of requirement gathering, product development, testing & quality assurance, deployment, and continuous maintenance and improvements. Based on these ALM disciplines, applications could build using software development practices such as Waterfall, Agile, or DevOps. ALM tools integrate the people and processes that support establishing good communication channels between all teams. Moreover, these tools help create a standardized working environment, and they also automate processes such as testing, delivery, and deployment.
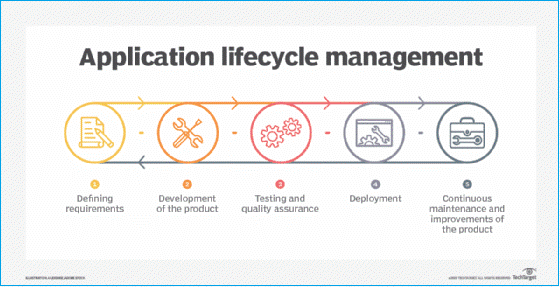
Image source: TechTarget
Before ALM fused people, tools, and processes, multiple teams managed different processes using different tools. Therefore, software development can be considered as a collection of separated processes. Business analysts are responsible for collecting the customer requirements and developers involved in designing and developing the product. After the testing phase, the product transfers to the IT support team for deployment and maintenance. ALM has changed this method by fusing all the above elements.
ALM vs. SDLC
Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) is involved-in in cost-effectively building high-quality software applications. While SDLC focuses on the development aspect of the application, ALM’s scope expands beyond that and covers the entire lifecycle of the application. ALM's role doesn’t end with the development phase but remains until the termination of the operations, which sometimes takes several years.
Three stages of Application Lifecycle Management
Though the implementation process changes on organization structure, the basic structure of the ALM framework can divide into three stages; governance, development, and operations. Each of these components has a distinctive role in the application lifecycle, and they integrate to deliver a quality product and continue the maintenance activities.
Application Governance
Stakeholders expect to fulfill their business requirements by adopting a new software application. The governance stage begins with the requirement definition and then moves to design the application. This phase ensures that software features meet the stakeholders’ business strategies. Requirement definition consists of both stakeholders’ business needs and compliance requirements of regulatory bodies. Decisions that take in this stage affect every aspect of the application, and this is the only stage that extends throughout the entire application lifecycle. Resource management, data security, and user access are the other elements of this stage. It is possible to automate the governance processes to streamline the ALM.
Application Development
Application development is the stage where the SDLC puts into action. Developers begin to code the system designed in the governance stage. After the development, the application needs to test against the requirements described in the governance stage. Different testing techniques can use to test the application before release to the production environment. Other types of development methodologies (Waterfall, Agile, or DevOps) can select in this stage based on the project’s goals. The continuous integration approach often uses by developers to speed up the development cycle. Many ALM tools provide the integrated source code management capabilities.
Application Operation
IT support team responsible for doing necessary maintenance and updates from time to time. The application operation stage is accountable for monitoring and managing all operations after the deployment. The remaining bugs identify in this stage report back to the development team to fix, and software updates will plan according to the changing business requirements. Different monitoring tools are used to measure and analyze the performance of the application. This stage will continue till the retirement of the application. Customer support, security monitoring, and reporting are other elements of the application operation stage.
Benefits of ALM
Productivity
ALM helps to increase the productivity of the development teams. ALM provides advanced tools to integrate the people and previously separated SDLC processes. These tools create effective communication between team members and will increase the productivity of the development cycle.
Speed
To stay competitive in the market, it’s essential to faster delivery of products. ALM speeds up the software development by enabling integrate source code management capabilities. In addition, integrated tools and processes enhance the efficiency of the overall application lifecycle.
Customer satisfaction
Maintenance and system support are some essential services that customers expect from IT support teams. ALM enhances customer satisfaction by the faster release of bug-free applications and providing continuous maintenance and support services.
Decision making
ALM concerns about the entire lifecycle of the application. ALM tools provide features to plan the future of the application until its termination. Features like version control and real-time planning help to do it better. Taking decisions in advance helps to utilize resources effectively and to prevent unnecessary investments in the future.
Visibility
Integrated tools and processes provide broad visibility to all stakeholders over the entire application lifecycle. They can observe and take decisions based on the real-time status of the project.
ALM tools
ALM tools make possible the easier management of application lifecycle processes. These processes include requirement management, development, testing and quality assurance, deployment, and support and maintenance. The main components that integrate these processes and people are ALM tools. These tools also support automating development, test, and deployment processes.
These are some of the popular ALM tools:
- Atlassian JIRA
- Inflectra Spirateam
- Micro Focus ALM Octane
- Tuleap
- CollabNet TeamForge
- Rally
- Helix ALM


