
Managing servers is a complex and challenging process. IT admins often complain that they have to spend a lot of time managing their servers on a daily basis. They also have to keep up-to-date with the latest security and compliance guidances to ensure the servers are secure. It’s also challenging to manage environments that span different platforms, including on-premises and in the Cloud. New features are always getting released, and therefore, keeping pace with the new cloud technologies becomes a difficult task. Spending the time to understand how to onboard and configure everything is also very time-consuming. Microsoft introduces Azure Automanage to address these customer challenges, and therefore, customers can focus their time on other innovative areas. Azure Automange is a service that helps automate daily management tasks for servers throughout their entire lifetime. In addition to the unique Windows Server capabilities, Automanage also configures and monitors machines with best-practice services that help reduce the time that you need to spend managing your fleet.
This is a list of best practice services that Automanage configures for you. It includes Azure Backup, Azure Security Center, Monitoring, Update management, and more.

In Cloud Adoption Framework for Azure section, under Best practices, and Azure server management services, there are a lot of options to help you understand how to get started, how to enable different Azure services on a single VM, how to do ongoing Cloud operations, etc.
Enable Azure Automanage for VMs in the Azure Portal
Sign in to the Azure Portal to start with Azure Automanage. Go to the search bar, type Automanage, and select the option for Automanage – Azure machine best practices. On the next page, you can see your subscription, and in the beginning, there are no Automanage VMs to display.
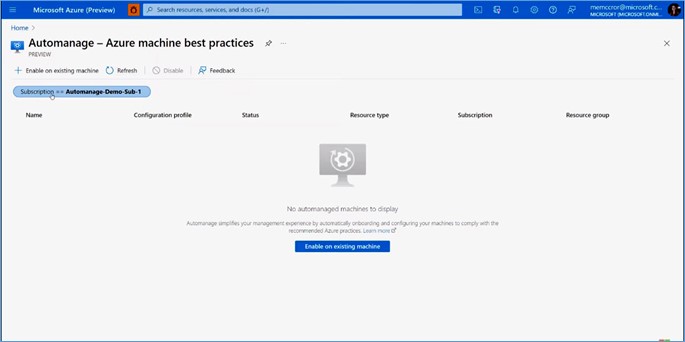
Click on the Enable on existing machine button.
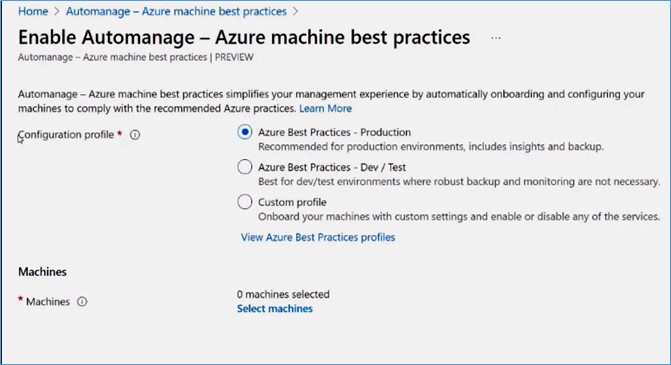
On the next page, there are two properties: Configuration profile and Machines. Under the Configuration profile, you can see three options: Azure Best Practices - Production profile, Azure Best Practices - Dev/Test profile, and Custom profile.
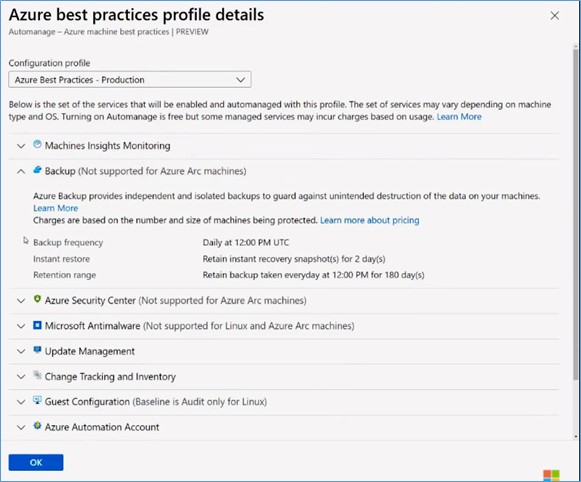
You can view the Azure Best Practices profiles to understand more about them. Under the Azure Best Practices – Production profile, you can see a list of services that will be onboarded and configured to any machine you select with this given profile. For instance, if you click the Backup service, you can see the properties that it will use to install Azure Backup for your given machines.
Under the Azure Best Practices – Dev/Test profile, you can see a list of services similar to the production profile. But, there are some differences between the production and Dev/Test profile. For instance, Azure Backup is not available in Dev/Test profile because you might not need to back it up on a daily basis, and it will reduce the cost.
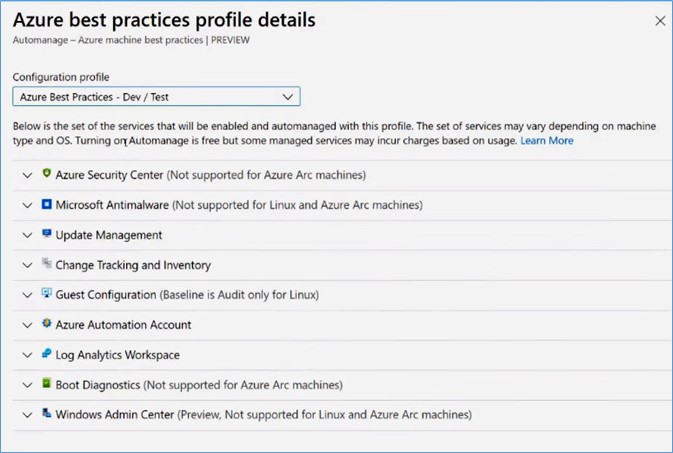
However, if your IT requirements are different from these best practices, you can create your own custom profile which you can pick and choose from this list of services. For instance, you can use your own antimalware solution instead of the Microsoft antimalware solution.
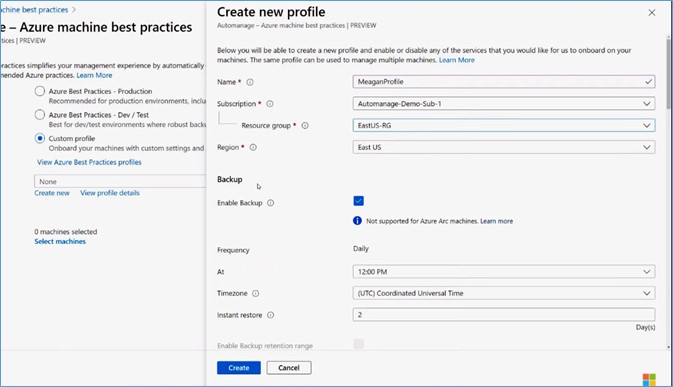
Create a Custom profile
Select the Custom profile and click on the Create new. Enter a profile name and select a resource group.
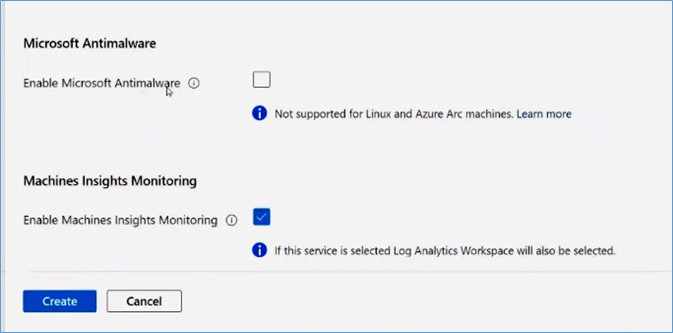
Since you want to use your own antimalware solution, uncheck the Enable Microsoft Antimalware checkbox, and this will not apply to the machines you select when creating the profile. If necessary, you can remove any other Azure services from this list.
Next, click on the Create button to create the profile.
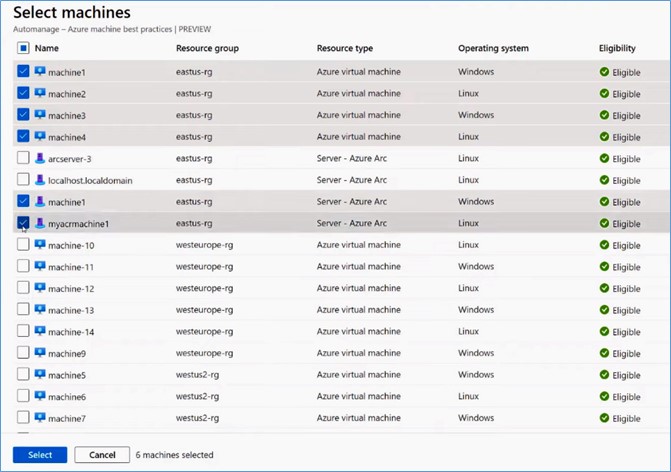
Next, click on Select machines.
There, you can see your subscription name (Automanage-Demo-Sub-1) and a list of machines. Machines’ operating system can be Windows or Linux-based, and their resource type includes Azure virtual machine, Server – Azure Arc, etc. Azure Arc allows you to take advantage of Azure services whether your machines run on-premises or in the Cloud. For instance, you can use Azure monitoring to monitor all of the machines and check the given statuses of your entire fleet.
Select a few machines from the list and click the Select button.
Next, click the Enable button and then you can see that your profile is being assigned to the machines that you selected before.

After that, you can see the selected machines and their properties such as configuration profile, status, resource type, etc.
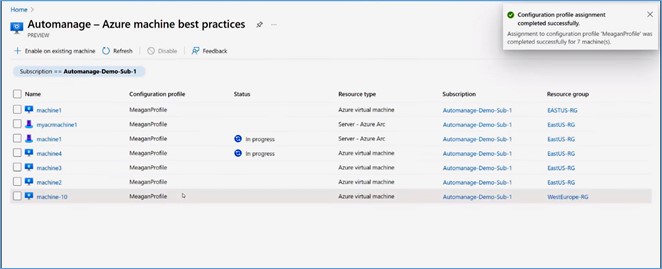
You should remember that Automanage does not only configure the machines as you want. It also monitors all of these services to make sure that they stay configured. For instance, if the monitoring extension gets removed accidentally on your given machine, Automanage will pick that up, and it will try to re-install that extension in order for monitoring to work correctly and make sure that it’s always connected to the given machine.
Let’s check on another scenario. Here, you can see a list of machines that have already been configured. Machine statuses appear with the green checkmark indicating that machines are conformant to the profile assigned to them. For instance, machines are conformant to either production profile or Dev/Test profile. Some are even conformant to the custom profiles as well.
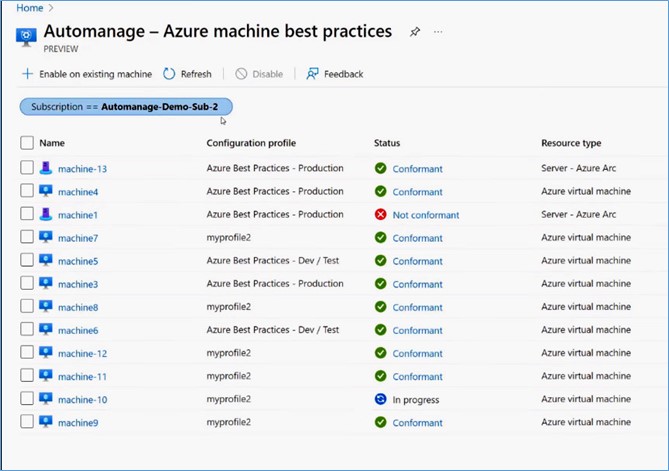
Here, you can notice that machine1 is not conformant. In this case, Automanage cannot perform some actions to ensure that all services are configured. To get more information, click on that status, and it will direct you to the Status Report. In that report, you can see the information such as when it started to be the non-conformant, the error that caused the non-conformant status, etc.
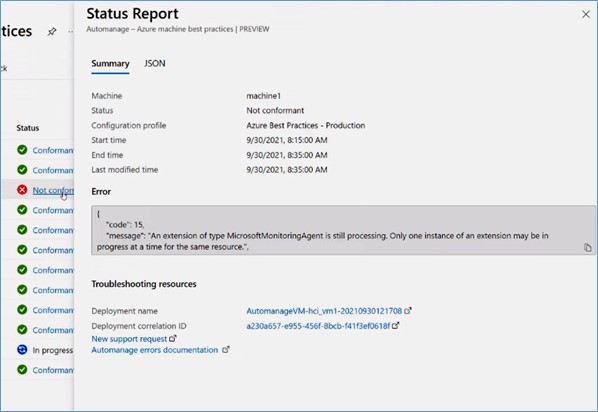
To troubleshoot further, you can look at the Deployment name or Deployment correlation ID, and these will contain the logs where you can troubleshoot the error. You could even create a new support request which will have all of the details of the error and get some support to troubleshoot further.
Key takeaways of Azure Automanage machine best practices
Automanage automatically onboards and configures your machines to the selected best-practice services. One of those services is the Microsoft Guests Configuration Service, which supports Microsoft security baselines on your given operating system. Not only does Automanage apply Azure services, but it will also apply the Microsoft security baselines inside your given operating system. Microsoft also supports flexibility through that custom profile option, so you can pick and choose the Azure best-practices services that fit your IT requirements. Automanage automatically monitors the services and if one of them drifts from the desired configuration, it will be rectified.
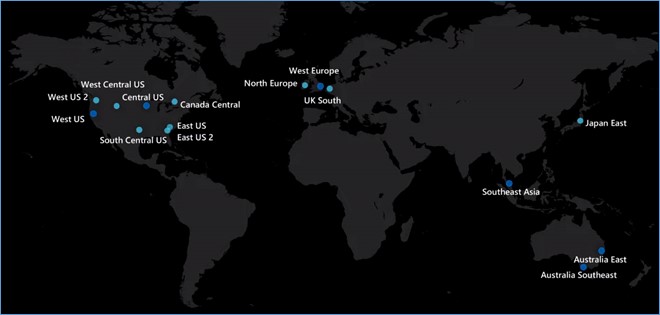
This is the list of supported regions where Automanage is available. If you have any machines in these regions, you can try out Automanage today.
Automanage is a simple experience, and Microsoft supports Windows VMs running in Azure, where you can apply Automanage. You can use Automanage on both Windows and Linux VMs running anywhere, and you also can fully customize the services through custom profiles. Automanage is a free offering. So, when you apply Automanage, there are no additional fees for using it. Though some services such as Azure Backup can incur a cost, the Automanage itself is free.
Reference:
Microsoft Ignite Sessions















