
In recent years, the growth of data exponentially increased with the new technological advancements such as Internet of Things (IoT), Cloud computing, Artificial Intelligence (AI), etc. Almost every digital platform turned into a source of data. Traditional data management infrastructures are not adequate to handle these large amounts of data as they grow. Also, a number of characteristics related to big data have been identified, including data that can be structured or unstructured, located in multiple on-premises or public/private cloud storages, and consists of different data types and file formats. These conditions create a diverse, distributed, and complex IT environment for enterprises and also create challenges such as data silos, security risks, decision-making issues, and data integration problems. For instance, an enterprise can use different public clouds such as AWS and Microsoft Azure to store their corporate data. But, it becomes difficult to share data between these cloud services or between cloud services and on-premises databases. As these challenges increase, data scientists have to spend more of their time solving them than examining and extracting insights from the data. Therefore, enterprises adopt modern data management solutions to mitigate these challenges and achieve their business goals. Data fabric came as a solution to help enterprises manage their dispersed and disparate data. Gartner, a research firm, included data fabric in their Top 10 Data and Analytics Technology Trends for 2021.
What is Data Fabric?
Data fabric is a single environment that uses a unified architecture consisting of an integrated set of technologies and services that helps enterprises to manage their data.
Gartner defines “data fabric as a design concept that serves as an integrated layer (fabric) of data and connecting processes. A data fabric utilizes continuous analytics over existing, discoverable, and inferenced metadata assets to support the design, deployment, and utilization of integrated and reusable data across all environments, including hybrid and multi-cloud platforms.”
The term “Data Fabric” was first introduced by NetApp, a hybrid cloud data services and data management company, in 2016. In a white paper titled “NetApp Data Fabric Architecture Fundamentals,” they discussed the new data management challenges that emerged in hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Enterprises deploy databases to store the data generated from data platforms that link to different business operations. For instance, a company may use separate databases to store the data generated in data platforms such as customer, supply chain, finance, human resource, etc. This architecture makes it difficult for data scientists to extract data from various sources and make decisions based on them. Data fabric allows them to see data belonging to different platforms more cohesively to make better decisions. It can extend to create new connections between data sources that help extract more insights from the data. In that manner, data fabric transforms the raw or primary data into meaningful business intelligence. It’s required to know new technologies such as semantic knowledge graphs, active metadata management, and embedded machine learning in order to understand the data fabric design.
Why a Data Fabric?
Enterprises use different methods to store data including relational databases, NoSQL or non-relational databases, data repositories, and flat files. Before data fabric, enterprises couldn't easily extract data from these sources for data-centric decision makings and data management also became a complex process. Traditional data management technologies cannot ensure consistency across different data sources and are not capable of finding the business-relevant connection between those data sources.
A data fabric simplifies accessing, ingesting, integrating, and sharing data across an enterprise in a governed manner, in real-time. Its network-based architecture manipulates data using connections instead of copies and allows enterprises to use data to make smart business-relevant decisions without changing their existing database architecture. Data virtualization is the technology that connects various data sources to create a virtual data layer by integrating metadata. But sometimes, data fabric requires copying data. For that, the data fabric should have robust data integration tools or ETL tools.
Gartner predicts that by 2024, 25% of data management solutions will have data fabric frameworks. Another research predicts that the market for data fabric software will grow up to $3.7 billion by 2026, from $1.1 billion in 2020. Some data fabric tools and software include;
Atlan
Cinchy
Data.world
Denodo
IBM Cloud Pak for Data
K2View
Implementation of Data Fabric
Enterprises face various challenges when implementing a data fabric solution, such as different data management policies, storage locations, and databases. Business needs also vary from one enterprise to another, and because of that, they need different data management solutions to achieve their business goals. As a result, a standard architecture for data fabric solutions cannot be defined. But, some common features among them can be identified.
Forrester mentioned six fundamental components of a data fabric in their “Enterprise Data Fabric Enables DataOps” report.
- Data management layer: Responsible for data governance and security of data.
- Data ingestion layer: Stitching cloud data together and finding connections between structured and unstructured data.
- Data processing layer: Refines the data to ensure that only relevant data is surfaced for data extraction.
- Data orchestration layer: Conducts data transformation, integrating and cleansing to make them usable for teams across the business.
- Data discovery layer: Surfaces new opportunities to integrate disparate data sources.
- Data access layer: Allows for the consumption of data, ensuring the right permissions for teams to comply with government regulations. This layer helps surface relevant data through the dashboards and other data visualization tools.
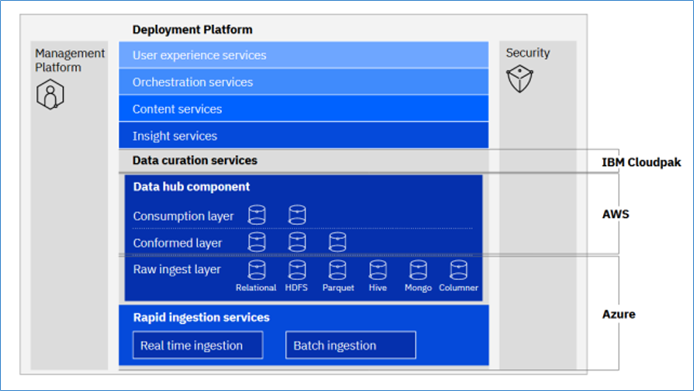
Image source: https://www.ibm.com/topics/data-fabric
Benefits of Data Fabric
Data Fabric allows enterprises to gain maximum benefits from their corporate data and helps them to speed up digital transformation. Some of the prominent benefits of data fabric include;
Eliminate data silos
A data silo is a collection of raw data that only permits access to one department of enterprises and is isolated from the rest. Each data silo consists of data belonging to different types and formats. The unified architecture of the data fabric enables other departments to have frictionless access to that data.
Automate data governance
Data fabric uses artificial intelligence to automate the process of applying corporate policies and data governance regulations to the data. For instance, data fabric can mask certain aspects of datasets, or some data can be redacted. This allows enterprises to deliver trusted data.
Facilitate data integration
Artificial intelligence and metadata facilitate data fabric to automate the data integration process. It accelerates the data delivery within enterprises in order to enable real-time insights.
Reference:
https://www.ibm.com/topics/data-fabric


