
What is a SAN?
A Storage Area Network (SAN) is a high-speed network that enables access to data storage at different levels. It involves connecting multiple storage devices to create a high-performance, low-latency, and scalable block storage solution. SAN addresses the need for expanding storage capacity independently from compute resources. In a hyper-converged stack, storage and compute resources are scaled up simultaneously. However, this approach often leads to CPU resource wastage, especially for data-intensive workloads that initially saturate the storage pipeline.
To overcome this challenge, SAN has introduced with flash array appliances, which have gained widespread adoption among enterprise customers in their on-premises data centers. These SAN appliances are available in various sizes, ranging from hundreds of terabytes to millions of IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second) and gigabytes of throughput. They offer a competitive total cost of ownership in bulk purchasing models. SAN is widely adopted in on-premises data centers for hosting hyper-scale databases, virtualization environments, Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI), and any IOPS-intensive applications.
Using SAN with the Cloud
As block storage offerings have evolved over the years, significant improvements have been made in scale, performance, and cost efficiency. However, customers often express challenges when migrating data stored in their on-premises SAN appliances to the Cloud. That's because existing block storage options provided by Cloud providers have dedicated performance targets for each individual volume or storage unit, with no resource sharing across volumes.
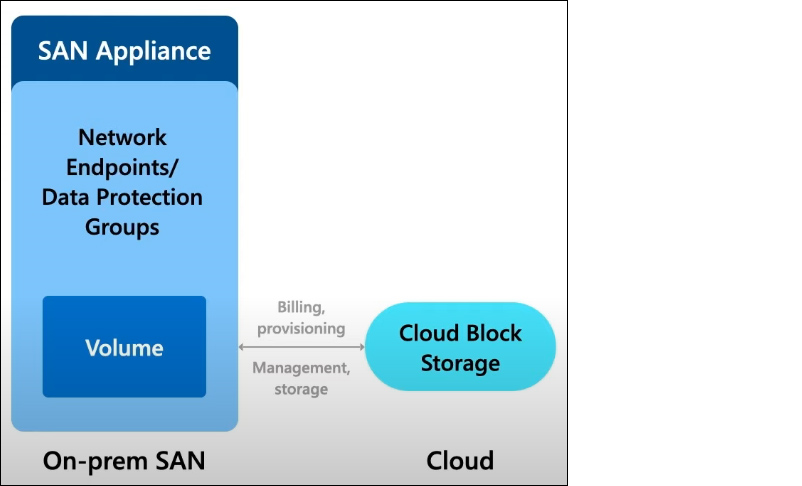
In an on-premises SAN setup, where all volumes reside in a single storage box, the performance of the SAN appliance is shared. It allows for balancing out IO spikes per individual volume and maintaining a stable level of IO traffic. In the Cloud, provisioning needs to be done for the maximum expected throughput per volume to avoid potential bottlenecks in the system. This means that there is no single block storage offering that works for different compute environments. As customers adopt the Cloud, they desire the flexibility to leverage different compute options for their workloads while having one consolidated block storage solution for simplified management. There are thousands of volumes for different workloads on a typical SAN appliance. It could be time-consuming if the Cloud migration requires the correct sizing for each volume. To address these pain points and accelerate the migration of SAN to the Cloud, Azure has introduced Azure Elastic SAN, a fully managed SAN offering in the Cloud.
Azure Elastic SAN
Azure Elastic SAN supports a resource hierarchy that resembles an on-premises SAN infrastructure. Resource provisioning occurs at the SAN level. Below the SAN level, there are volume groups that serve as a grouping mechanism for applying configurations related to security, networking, and data protection. The volume serves as the fundamental data storage unit, similar to storage found in on-premises environments.
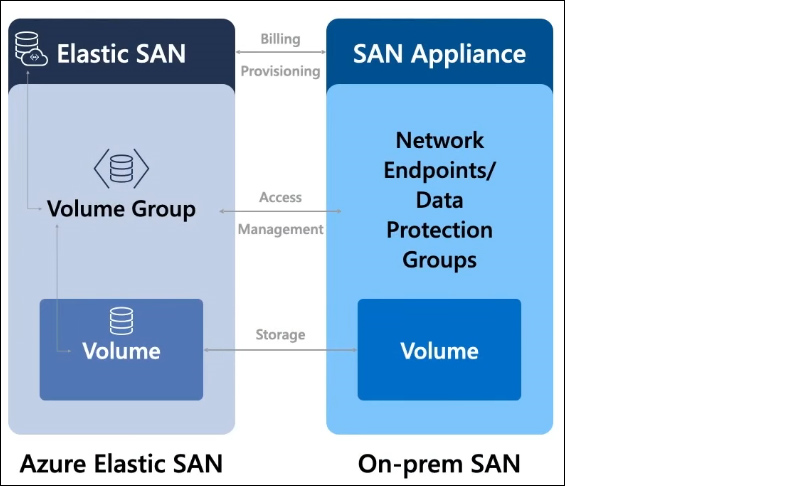
Azure Elastic SAN enables customers to deploy, manage, and host workloads on Azure, providing an end-to-end experience similar to on-premises environments while minimizing adoption friction. Storage provisioning takes place at the SAN level, enabling customers to achieve massive scalability in terms of millions of IOPS and double-digit gigabytes per second. The volume group concept simplifies volume management, allowing users to apply configuration changes at the group level, thereby reducing the management overheads.
Azure Elastic SAN fully supports iSCSI for data access to volumes, a widely adopted standard protocol for various workloads. Both Linux and Windows operating systems include built-in drivers that support the connection to block storage via iSCSI. Azure Elastic SAN offers an alternative path for SAN migration, driven by specific storage requirements, providing a seamless transition to the Cloud.
On-premises vs. Azure Elastic SAN user journey
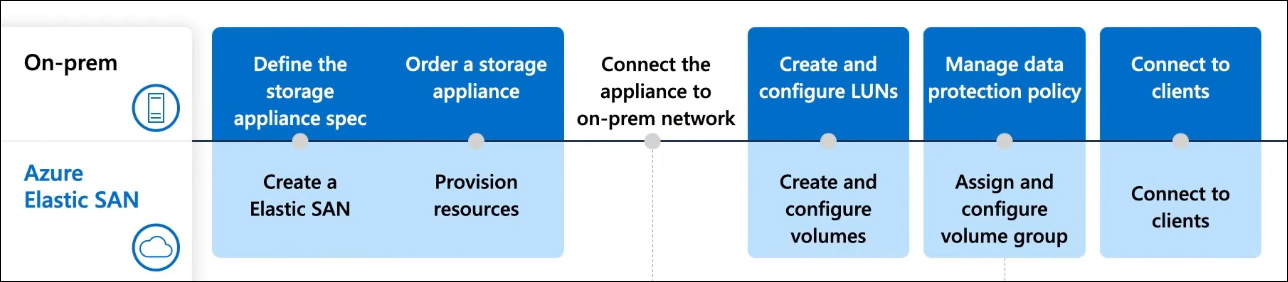
When comparing creating an Azure Elastic SAN with on-premises SAN deployments, it becomes evident that Azure Elastic SAN follows a similar workflow. However, Azure Elastic SAN offers the added advantage of leveraging the Cloud. Instead of enduring months of waiting to order storage hardware, you can swiftly deploy and scale up an Azure Elastic SAN with just a few clicks on Azure. Furthermore, security and network configurations of your storage have been simplified by introducing the management group as a volume group. This means that any configuration changes made at the group level will directly propagate to all volumes.
Azure Block Storage for every workload
With the introduction of Azure Elastic SAN, the block storage portfolio extends to accommodate a wide range of workload requirements. There are Azure disks that offer optimized solutions for virtual machines ranging from standard HDDs to high-performance Ultra Disk. On the other hand, Azure Elastic SAN sets new standards for scalability in Cloud block storage. During the initial public preview, a SAN-level capacity of two million IOPS and 32,000 MB/s is available, with plans to further enhance these capabilities. The provision target on the SAN can dynamically share across volumes. This allows individual volumes to achieve a minimum deployment of 64,000 IOPS and 1000 MB/s.
Azure Elastic SAN overview
Azure Elastic SAN comprises three layers of resources: Elastic SAN, Volume Group, and Volume. At the top level, Elastic SAN resource for provisioning and billing. Below that, the volume group offers a grouping mechanism similar to resource groups, enabling the application of configurations at the volume group level that are enforced across all volumes. Finally, Volumes serve as individual storage units where data gets written.
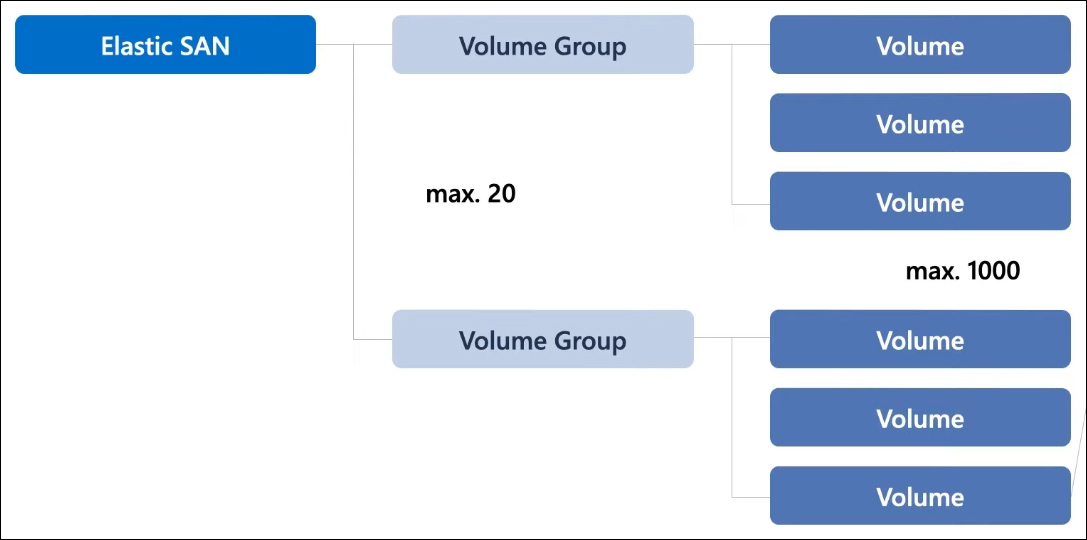
Elastic SAN
When deploying an Elastic SAN, the provisioning workflow begins at the SAN level. Two provisioning units are available for composing your SAN, namely the base unit and the capacity-only unit. These units are designed to offer a simple bulk provisioning experience while allowing flexibility for scaling your data footprint. The base unit provides both capacity and provision performance, while the capacity-only unit enables you to pay for capacity alone at a lower price. It's important to note that the provisioned resources at the SAN level share across all volume groups and volumes. In addition to the two provisioning units, redundancy options are provided to meet specific durability and availability requirements for storage.
Volume Group
Storage administrators can utilize volume groups as containers for volumes that dedicate to specific workloads. By grouping volumes, they can apply encryption and network security settings at the group level, which will propagate to all volumes within that group. It is worth noting that a SAN can accommodate up to 20 volume groups.
Volume Group: Network security rules
During the public preview phase of Azure Elastic SAN, network security rules have been leveraged to restrict client access to volumes. By default, network access to volumes within a volume group is denied, mitigating the risk of deploying publicly accessible volumes. Administrators have the flexibility to configure network security rules to grant access to clients from specific virtual networks. For example, when volumes deploy for an AKS cluster, a rule can be added to unblock network access from the virtual network where AKS deploys. This enables clients within that virtual network to connect to any volumes in the group using iSCSI. If you are familiar with network security settings on Azure storage accounts, this concept is similar to enabling your account for public network access from selected virtual networks. This step is necessary to unblock the iSCSI connection to a volume.
Volume
Volume is the primary storage unit for reading and writing data in Azure Elastic SAN. Azure supports data access to volume through the widely adopted iSCSI protocol. Windows and Linux operating systems include inbox drivers facilitating connections to iSCSI targets. The performance of a volume scales linearly with its capacity. However, Azure has designed the scaling factors to be sufficiently high, alleviating concerns about performance. Achieving the maximum performance target of 64,000 IOPS and 1000 MB/s requires a volume size of around 100GB.
It's important to note that all volumes share the provisioned performance at the SAN level. However, there is no need to provision the SAN level target to match the sum of all volumes. For example, you can provision 500,000 IOPS at the SAN level and deploy 1TB volume (10x), each capable of reaching a maximum of 64,000 IOPS. Though the total of all volumes' maximum IOPS reaches 640,000, it is unnecessary to fully provision that capacity at the SAN level since it is unlikely that all volumes will reach their maximum target simultaneously.
Creating an Elastic SAN
Here you can see the entire workflow for creating an Elastic SAN.
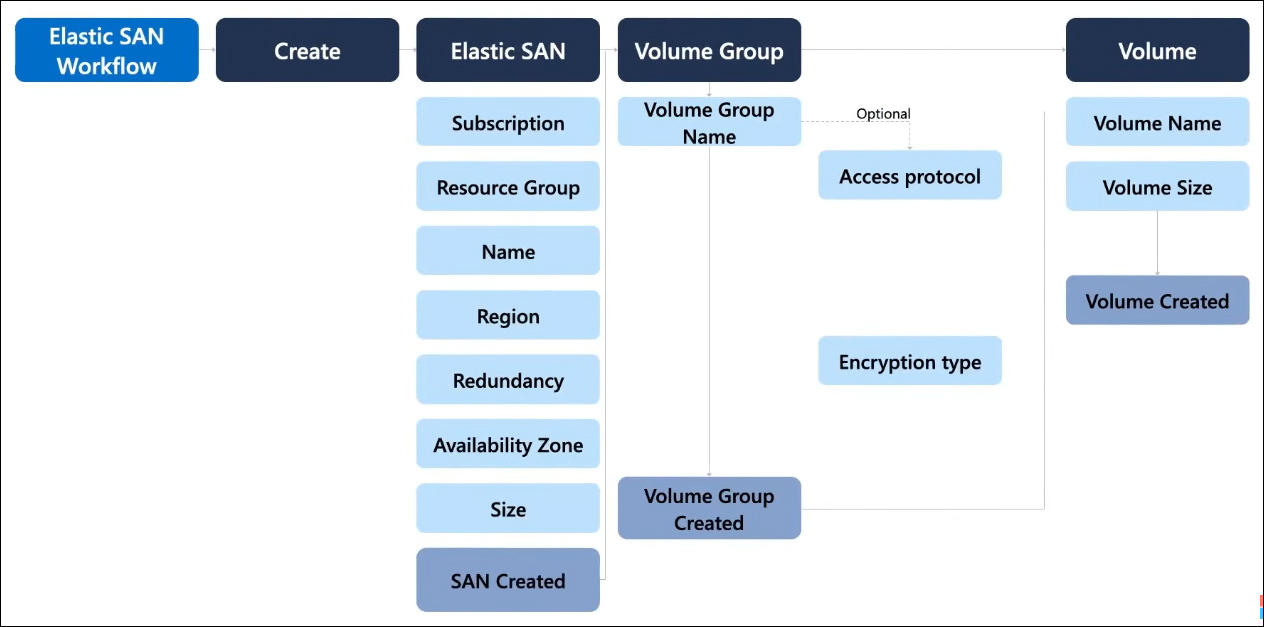
Resources are provisioned at the SAN level. When you fill out the information, you should precisely know the workload you intend to host. It will allow you to determine the respective capacity and performance requirements. Once you have gathered this information, you can proceed with provisioning the storage and performance accordingly. The workflow for setting up the SAN involves several steps. First, you create the SAN itself. Then, you proceed to create the volume groups and finally create individual volumes for storing your data.
Consolidate your storage and achieve cost efficiency at scale
Azure Elastic SAN utilizes a resource hierarchy similar to on-premises SAN, providing a consolidated and familiar management experience. Network and encryption configurations are applied at the volume group level, ensuring consistency across all volumes within the group. This streamlined approach not only simplifies management but also offers cost efficiency when deploying block storage at scale. You can share the provisioned performance of your Elastic SAN across multiple volumes, enabling you to achieve high performance while optimizing costs. For example, by deploying a 100TB Elastic SAN with 500,000 IOPS, you can dynamically allocate these IOPS across 1TB (100x) volumes, with each volume reaching a maximum of 64,000 IOPS. This flexibility allows you to efficiently utilize available performance based on the specific needs of each volume. Additionally, Azure Elastic SAN offers capacity units that provide only storage. This means that if you require additional storage beyond your initial provisioning, you can easily purchase extra capacity at a significantly lower price than purchasing additional performance resources.
Integrate with your choice of compute options
Azure Elastic SAN supports industry-standard iSCSI protocol, enabling connectivity to various Azure compute options, such as virtual machines and containers. Even if you run workloads in non-VM-based environments, Azure Elastic SAN offers the flexibility to migrate your SAN workloads to the Cloud.
Drive higher storage throughput over network-attached storage
When dealing with workloads that demand high throughput, you may encounter limitations imposed by the disk throughput of your VM. For example, if you are utilizing an Azure Standard_E104_v5 VM, which is constrained to 120,000 IOPS and 4000 MB/s. However, there are scenarios where you require exceptionally high throughput to complete the data processing in time. With Azure Elastic SAN, you can achieve high throughput by leveraging the VM network bandwidth, reaching speeds up to 100,000 Mbps. This provides an additional 12,500 MB/s of throughput over the wire.
Azure Elastic SAN will support more compute options and improve scalability, performance, and latency. Service management and security capabilities will be enhanced with iSCSI support, server-side encryption with customer-managed key, and private endpoint support. Backup and disaster recovery features will also be added, including incremental snapshots and snapshot export.
Useful links
What is Azure Elastic SAN? Preview
Plan for deploying an Elastic SAN Preview
Azure Elastic SAN PREVIEW pricing
Reference
Microsoft Ignite Sessions







